Characterization of leaf phenotypic traits in natural populations of three Polyspora species
-
摘要:
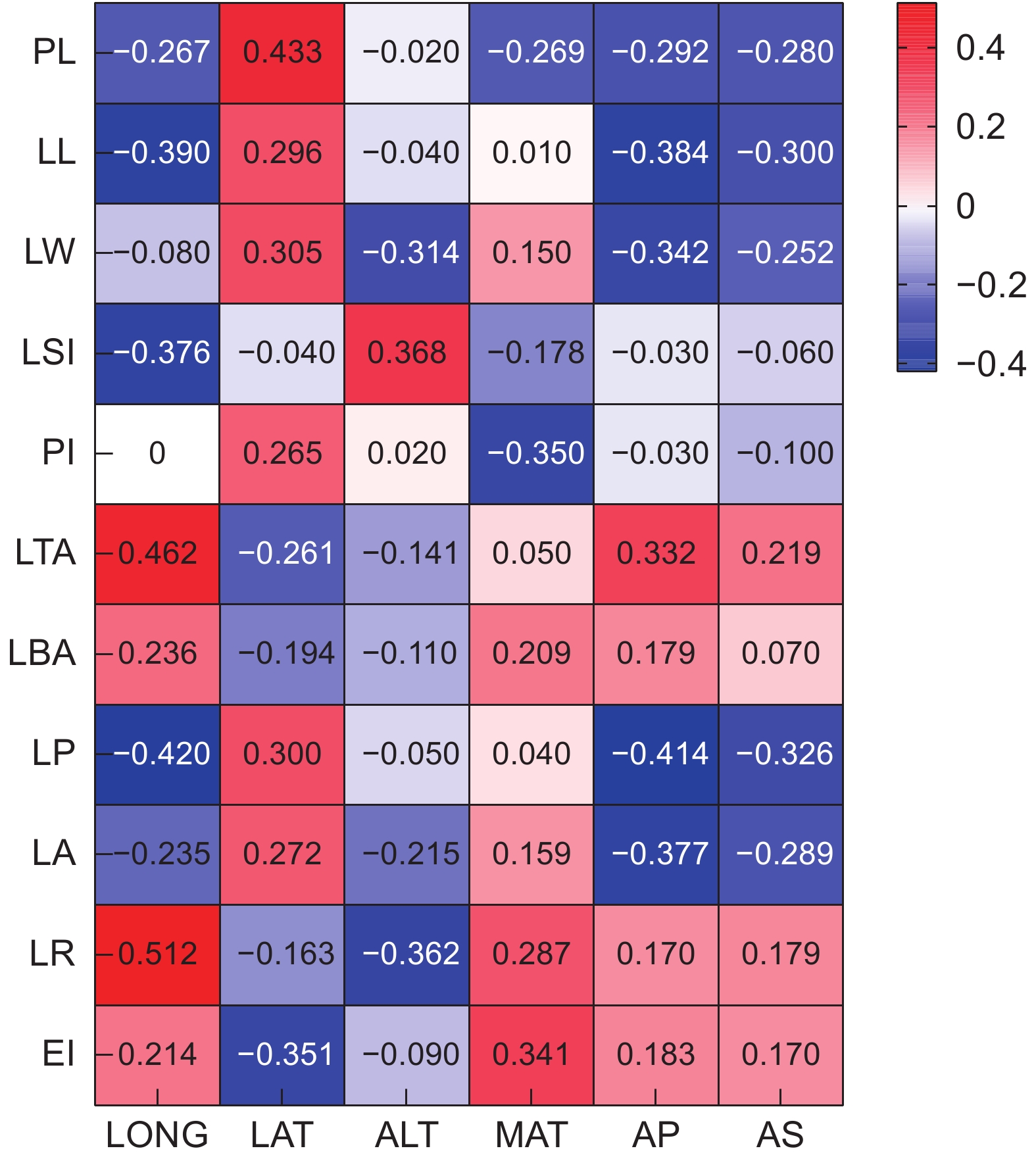
以大头茶属(Polyspora)3种植物的10个天然居群为研究对象,通过多重比较、巢式方差分析、相关性分析、主成分分析和聚类分析等方法,对11个叶表型性状的变异规律进行研究。结果显示:(1)叶表型性状在居群内和居群间均存在极显著差异(P<0.01),平均变异系数为17.03%,不同性状的变异幅度为0.05%~31.37%。叶表型性状在居群内和居群间的方差分量均值分别为180.79和82.63,表明叶表型性状分化程度为居群内高于居群间。(2)叶宽、叶柄长、叶面积、叶基角、叶圆度和叶柄指数为叶表型变异的主导因素;各表型性状之间存在明显的相关性,环境因子对大头茶属植物叶表型性状变异的影响很大;基于叶表型性状可将10个居群分为3类。研究结果可为大头茶属植物的适应性进化和开发利用提供理论依据。
Abstract:Leaf phenotypic variation among 10 populations of three Polyspora species was analyzed using multiple comparisons, nested variance analysis, correlation analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), and cluster analysis. Results revealed: (1) Significant differences in leaf phenotypic traits both within and among Polyspora populations (P<0.01). The average coefficient of variation was 17.03%, with trait-specific variation ranging from 0.05% to 31.37%. Mean variance components for leaf traits were higher within populations (180.79) than among populations (82.63), indicating greater differentiation within populations. (2) Dominant contributors to phenotypic variation included leaf width, petiole length, leaf area, leaf base angle, leaf roundness, and petiole index. Significant correlations among leaf traits were identified, highlighting the strong influence of environmental factors on leaf phenotypic variation. Cluster analysis grouped the 10 populations into three distinct groups based on leaf phenotypic traits. The results provide valuable insights into the adaptive evolution and exploitation of Polyspora species.
-
Keywords:
- Leaf traits /
- Natural population /
- Phenotypic variation /
- Environmental factors /
- Polyspora
-
-
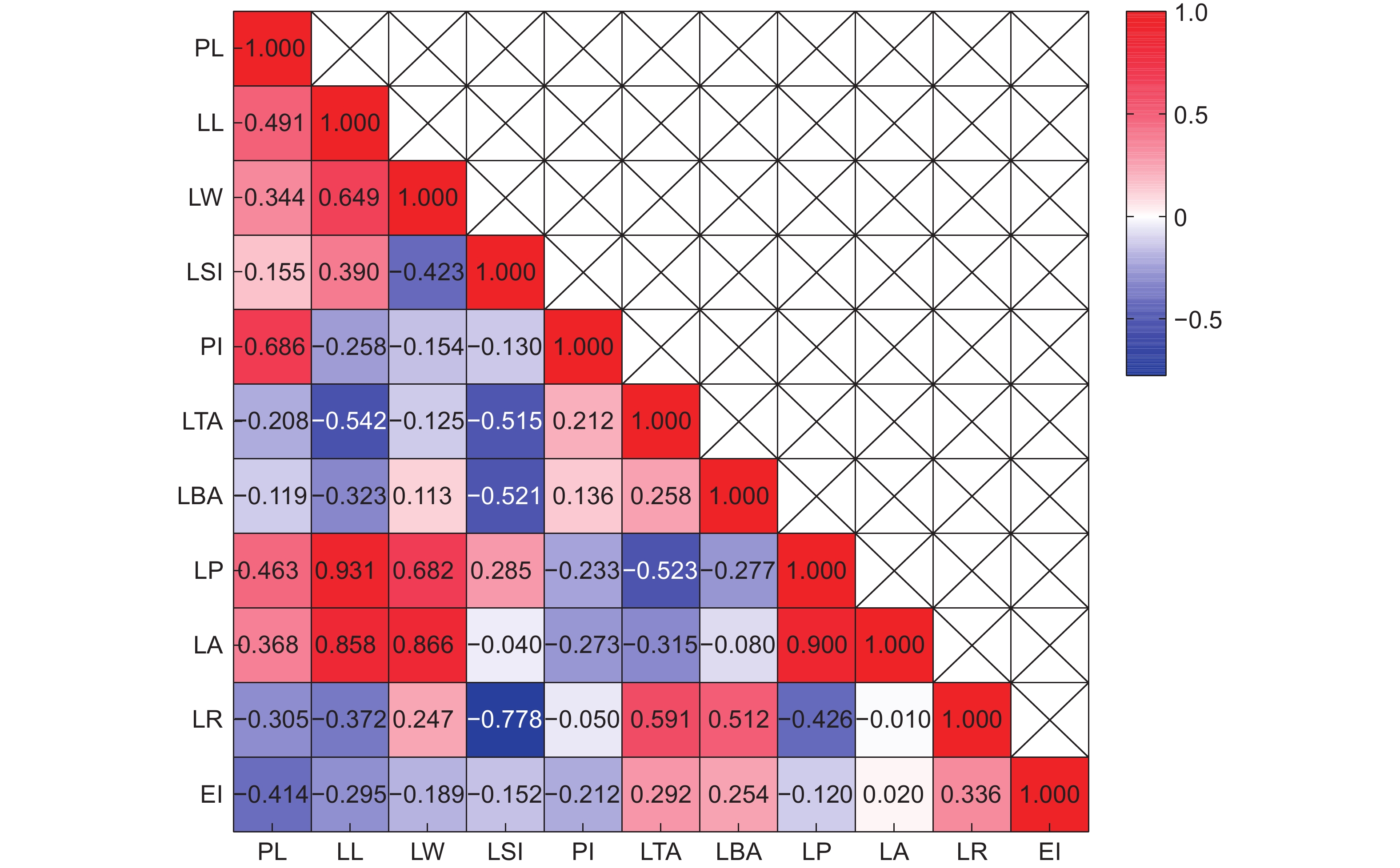
图 1 大头茶属植物叶表型性状相关性热图
PL:叶柄长;LL:叶长;LW:叶宽;LP:叶周长;LA:叶面积;LBA:叶基角;LTA:叶尖角;PI:叶柄指数;LSI:叶形指数;LR:叶圆度;EI:椭圆度。下同。
Figure 1. Correlation heatmap of leaf phenotypic traits in Polyspora
PL: Petiole length; LL: Leaf length; LW: Leaf width; LP: Leaf perimeter; LA: Leaf area; LBA: Leaf base angle; LTA: Leaf tip angle; PI: Petiole index; LSI: Leaf shape index; LR: Leaf roundnes; EI: Ellipticalness index. Same below.
表 1 大头茶属植物天然居群地理生态因子
Table 1 Geo-ecological factors of natural populations of Polyspora
序号
No.物种名称(株数)
Species (ind.)采集地点(代码)
Location (Code)纬度
Latitude
(LAT)经度
Longitude
(LONG)海拔
Altitude
(ALT) / m年均温
Mean annual temperature
(MAT)/ ℃年降水
Annual precipitation
(AP) / mm年日照
Annual sunshine
(AS) / h1 P. speciosa(22) 云南昭通盐津县(YJ) 28°2′6.51″N 104°10′44.18″E 946 17.0 676.3 966.0 2 P. speciosa(25) 重庆北碚缙云山(BB) 29°49′47.84″N 106°23′14.43″E 821 18.3 506.0 1 012.2 3 P. speciosa(24) 四川泸州叙永县(XY) 28°17′16.71″N 105°29′21.56″E 686 17.9 1 067.9 1 170.3 4 P. speciosa(21) 贵州遵义习水县(XS) 28°24′46.73″ N 106°36′4.98″E 1 370 17.0 1 933.6 1 269.0 5 P. kwangsiensis(20) 广西来宾金秀县(JX) 24°14′52.93″N 110°12′41.32″E 1 031 20.1 2 086.2 1 413.7 6 P. kwangsiensis(24) 广西桂林恭城县(GC) 24°59′53.27″N 110°56′23.30″E 460 19.9 1 558.1 1 549.1 7 P. kwangsiensis(24) 广西贺州平桂区(PG) 24°37′15.73″N 111°32′34.92″E 617 20.2 1 609.7 1 274.8 8 P. kwangsiensis(16) 广西百色那坡县(NP) 23°17′36.50″N 105°47′29.4″E 1 135 16.5 1 603.7 1 288.3 9 P. kwangsiensis(7) 广西桂林永福县(YF) 24°52′39.36″N 110°09′4.39″E 296 13.6 1 420.6 1 183.7 10 P. tonkinensis(22) 云南红河屏边县(PB) 22°54′38.64″ E 103°42′2.45″ N 2 048 18.8 1 545.6 1 937.3 表 2 大头茶属植物10个天然居群叶表型性状多重比较
Table 2 Multiple comparisons of leaf phenotypic traits among 10 natural populations of Polyspora
叶表型性状
Leaf
phenotypic
trait居群
PopulationYJ BB XY JX GC PG NP PB XS YF PL 22.33±4.06ab 21.30±4.53bc 20.35±4.77bcd 15.37±4.35g 17.86±3.63defg 17.26±3.29efg 19.72±4.61cde 16.78±3.29fg 24.68±5.58a 18.12±2.62def LL 251.28±21.98a 232.78±37.78b 219.20±36.93bc 165.05±19.96e 208.44±21.88cd 198.99±32.13d 222.36±36.36bc 211.72±26.61cd 208.37±49.64bc 199.34±17.73cd LW 69.45±9.20a 67.87±13.71ab 59.47±8.75c 52.96±11.01d 62.85±5.58bc 61.42±6.66c 61.37±9.60c 51.69±7.87d 57.46±13.30cd 59.95±10.88de LSI 3.66±0.41bc 3.47±0.43bcd 3.71±0.48b 3.25±0.78d 3.33±0.36cd 3.25±0.49d 3.66±0.59bc 4.14±0.49a 3.65±0.43ab 3.63±0.22bc PI 0.09±0.02abc 0.09±0.01abc 0.09±0.02abc 0.09±0.02ab 0.09±0.02bc 0.09±0.02bc 0.09±0.02bc 0.08±0.02c 0.12±0.03c 0.09±0.01d LTA 32.30±7.15e 32.52±9.82e 34.51±13.37de 62.96±23.85b 53.08±14.25c 60.33±20.50bc 42.89±14.81d 36.81±11.42de 50.60±15.33c 41.57±13.80d LBA 36.20±6.25e 55.57±7.04abc 47.21±10.15cd 62.43±22.83a 52.04±14.96bcd 55.19±12.30abc 60.66±19.16ab 45.58±12.13d 46.71±7.92d 47.37±10.17de LP 62.88±6.25a 57.14±9.76b 54.11±8.51bc 40.86±4.74e 50.94±4.56cd 48.21±6.90d 53.75±7.16bc 52.28±6.79c 48.64±10.56d 48.66±5.23cd LA 101.85±20.15a 94.13±25.26bc 79.04±24.07c 54.87±14.26e 80.63±13.18c 76.87±16.88cd 85.68±23.81bc 67.64±18.56d 67.99±30.13de 65.98±10.88e LR 0.32±0.03f 0.36±0.04cd 0.34±0.05de 0.41±0.07b 0.39±0.04bc 0.42±0.05b 0.37±0.06c 0.31±0.03f 0.35±0.05ef 0.35±0.03d EI 0.74±0.03e 0.76±0.06de 0.76±0.03de 0.80±0.03b 0.78±0.02bc 0.80±0.03b 0.79±0.03bc 0.78±0.03cd 0.71±0.13d 0.76±0.02de 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。PL:叶柄长;LL:叶长;LW:叶宽;LP:叶周长;LA:叶面积;LBA:叶基角;LTA:叶尖角;PI:叶柄指数;LSI:叶形指数;LR:叶圆度;EI:椭圆度。居群缩写为样本采集地代码,其含义与表1相同,下同。 Notes: Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant difference (P<0.05). PL: Petiole length; LL: Leaf length; LW: Leaf width; LP: Leaf perimeter; LA: Leaf area; LBA: Leaf base angle; LTA: Leaf tip angle; PI: Petiole index; LSI: Leaf shape index; LR: Leaf roundnes; EI: Ellipticalness index. Abbreviations of population indicate sampling locations as in Table 1. Same below. 表 3 大头茶属植物天然居群表型性状变异系数
Table 3 Coefficients of variation of phenotypic traits of natural populations of Polyspora
居群
Population叶表型性状变异系数Coefficients of variation of leaf phenotypic traits / % PL LL LW LSI PI LTA LBA LP LA LR EI 均值Mean YJ 17.80 8.57 12.98 11.11 20.17 21.69 16.93 9.75 19.39 7.75 0.04 13.29 BB 20.84 15.90 19.80 12.25 17.93 29.59 12.41 16.74 26.29 11.07 0.07 16.63 XY 22.95 16.51 14.41 12.67 19.67 37.97 21.06 15.4 29.83 14.43 0.04 18.63 JX 27.72 11.85 20.38 23.58 24.26 37.11 35.84 11.36 25.47 17.01 0.04 21.33 GC 19.92 10.29 8.70 10.50 17.40 26.30 28.17 8.77 16.02 9.92 0.02 14.18 PG 18.67 15.82 10.62 14.80 17.77 33.29 21.87 14.02 21.52 11.66 0.03 16.37 NP 22.89 16.02 15.32 15.79 20.33 33.84 30.94 13.05 27.23 15.88 0.03 19.21 PB 19.22 12.31 14.92 11.67 19.62 30.39 26.07 12.72 26.89 11.03 0.04 16.81 XS 22.60 23.82 23.15 11.80 21.04 30.30 16.96 21.70 44.32 13.53 0.18 20.85 YF 14.45 8.89 8.99 6.04 14.16 33.20 21.48 10.75 16.48 9.06 0.03 13.05 均值 20.70 14.00 14.93 13.02 19.24 31.37 23.17 13.43 25.34 12.13 0.05 17.03 表 4 大头茶属植物居群表型性状的巢式方差分析
Table 4 Nested variance analysis of phenotypic traits of populations of Polyspora
表型性状
Phenotypic trait均方Mean square F值 F value 居群间
Inter-population居群内
Intra-population居群间
Inter-population居群内
Intra-populationPL 202.340 8.760 11.111** 0.481 LL 13036.751 698.822 12.626** 0.677 LW 871.434 53.598 9.250** 0.569 LSI 1.780 0.175 7.226** 0.710 PI 0.003 0 9.233** 1.035 LTA 3 234.154 151.352 13.586** 0.636 LBA 1 547.572 90.130 8.298** 0.483 LP 871.083 31.426 15.609** 0.563 LA 4 947.772 268.632 11.261** 0.611 LR 0.034 0.002 15.320** 0.880 EI 0.019 0.002 7.377** 0.850 Note: **, P<0.01. 表 5 大头茶属植物叶表型性状的方差分量与表型分化系数
Table 5 Variance components and phenotypic differentiation coefficients of leaf phenotypic traits in Polyspora
表型性状
Phenotypic trait方差分量
Variance component方差分量百分比
Percentage of variance components / %表型分化系数
Phenotypic differentiation
coefficient / %居群间
Inter-population居群内
Intra-population随机误差
Random errors居群间
Inter-population居群内
Intra-populationPL 7.403 17.266 4.967 30.01 69.99 30.00 LL 481.503 999.186 38.480 32.52 67.48 32.52 LW 31.252 90.147 11.018 25.74 74.26 25.74 LSI 0.062 0.239 0.549 20.49 79.51 20.60 PI 0 0 0.021 24.70 75.30 0 LTA 120.191 229.373 18.697 34.38 65.62 34.38 LBA 54.829 176.858 15.221 23.66 76.34 23.67 LP 32.709 53.370 9.278 38.00 62.00 38.00 LA 181.019 422.297 24.562 30.00 70.00 30.00 LR 0.001 0.002 0.059 36.72 63.28 33.33 EI 0.001 0.002 0.056 20.61 79.39 33.33 均值 82.630 180.790 11.170 28.80 71.20 27.42 表 6 大头茶属植物叶表型性状的主成分分析
Table 6 Principal component analysis of leaf phenotypic traits of Polyspora
叶表型性状
Leaf phenotypic trait主成分Principal component PC1 PC2 PC3 PL 0.389 −0.151 0.868 LL 0.873 −0.427 0.083 LW 0.915 0.320 0.096 LSI −0.073 −0.918 −0.019 PI −0.278 0.174 0.897 LTA −0.363 0.673 0.006 LBA −0.053 0.686 0.003 LP 0.897 −0.371 0.042 LA 0.982 −0.002 −0.048 LR −0.018 0.896 −0.210 EI −0.115 0.312 −0.559 特征值 4.368 2.616 1.841 贡献率 / % 39.712 23.778 16.738 累计贡献率 / % 39.712 63.489 80.228 注:粗体表示该性状在PCA轴上的最大载荷。 Note: Bold indicates maximum load on PCA axis for the trait. -
[1] 张睿,国春策,山红艳,孔宏智. 发育重塑与生物多样性[J]. 生物多样性,2014,22(1):66−71. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13248 Zhang R,Guo CC,Shan HY,Kong HZ. Developmental repatterning and biodiversity[J]. Biodiversity Science,2014,22(1):66−71. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13248
[2] Li YG,Liu XH,Ma JW,Zhang XM,Xu LA. Phenotypic variation in Phoebe bournei populations preserved in the primary distribution area[J]. J FR,2018,29(1):35−44.
[3] Morton CV. Botany:Principles of Angiosperm Taxonomy. P. H. Davis and V. H. Heywood. Van Nostrand,Princeton,N. J. ,1963. xx + 556 pp. Illus. $15. [J]. Science,1964,144(3618):531.
[4] Wang ML,Zhang JX,Guo ZP,Guan YZ,Qu G, et al. Morphological variation in Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. ,and its relationship with the environment along a longitudinal gradient[J]. Hereditas,2020,157(1):4.
[5] 牛雪婧,聂靖,赵雪利,高信芬. 河北木蓝的叶表型可塑性研究[J]. 植物科学学报,2020,38(1):97−104. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2020.10097 Niu XJ,Nie J,Zhao XL,Gao XF. Leaf-level phenotypic plasticity of Indigofera bungeana Walp[J]. Plant Science Journal,2020,38(1):97−104. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2020.10097
[6] 郑孙元,朱弘,金思雨,王梦娟,孙杰,等. 桂花表型变化的环境依赖特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2019,43(2):38−46. Zheng SY,Zhu H,Jin SY,Wang MJ,Sun J,et al. Environment-dependent phenotypic variation of Osmanthus fragrans[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2019,43(2):38−46.
[7] 杨世雄. 国产大头茶属的分类处理[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2005,13(4):363−365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2005.04.017 Yang SX. Taxonomic treatment of Chinese Polyspora Sweet (Theaceae)[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2005,13(4):363−365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2005.04.017
[8] 马长乐,李靖,白琼,黄晓霞,程小毛. 云南省乡土树种大头茶属植物资源分布与利用探讨[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2015(5):78−80. Ma CL,Li J,Bai Q,Huang XX,Cheng XM. Distribution and utilization of the indigenous tree species of genus Polyspora in Yunnan province[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2015(5):78−80.
[9] 陈新艳. 福建省五种植物新记录[J]. 广西植物,2020,40(8):1127−1131. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201901022 Chen XY. New records of five species of plants in Fujian province[J]. Guihaia,2020,40(8):1127−1131. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201901022
[10] 樊智丰,韩露,马长乐. 大头茶属植物研究进展[J]. 广西植物,2021,41(10):1755−1766. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202010042 Fan ZF,Han L,Ma CL. Research advances of Polyspora Sweet (Theaceae)[J]. Guihaia,2021,41(10):1755−1766. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202010042
[11] 中华人民共和国生态环境部,中国科学院. 中国生物多样性红色名录——高等植物卷(2020)[M]. 北京:生态环境部,中国国科学院,2023:795,2356−2357. [12] Beech E,Barstow M,Rivers M. The Red List of Theaceae[M]. Richmond,UK:Botanic Gardens Conservation International,2017:32−37.
[13] Fan ZF,Qian SJ,Zhang YH,Ma CL. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Polyspora tiantangensis (Theaceae),an endemic and endangered species in southwestern China[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B,2021,6(3):814−815. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1884013
[14] 高灿,樊智丰,马长乐. 黄药大头茶叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性分析[J]. 西南林业大学学报,2023,43(5):66−76. doi: 10.11929/j.swfu.202203018 Gao C,Fan ZF,Ma CL. Analysis of codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of Polyspora chrysandra[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University,2023,43(5):66−76. doi: 10.11929/j.swfu.202203018
[15] Athukoralage PS,Herath HMTB,Deraniyagala SA,Wijesundera RLC,Weerasinghe PA. Antifungal constituent from Gordonia dassanayakei[J]. Fitoterapia,2001,72(5):565−567. doi: 10.1016/S0367-326X(00)00339-7
[16] Fu HZ,Li CJ,Yang JZ,Shen ZF,Zhang DM. Potential anti-inflammatory constituents of the stems of Gordonia chrysandra[J]. J Nat Prod,2011,74(5):1066−1072. doi: 10.1021/np200021f
[17] 穆兵,李茂,杨成华,邓伦秀,潘德权,等. 习水国家级自然保护区四川大头茶群落研究[J]. 种子,2011,30(12):62−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2011.12.018 Mu B,Li M,Yang CH,Deng LX,Pan DQ,et al. Study on Sichuan big head tea community in Xishui national nature reserve[J]. Seed,2011,30(12):62−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4705.2011.12.018
[18] Fan ZF,Zhou BJ,Ma CL,Gao C,Han DN,et al. Impacts of climate change on species distribution patterns of Polyspora Sweet in China[J]. Ecol Evol,2022,12(12):e9516. doi: 10.1002/ece3.9516
[19] Zhang Q,Zhao L,Folk RA,Zhao JL,Zamora NA,et al. Phylotranscriptomics of Theaceae:generic-level relationships,reticulation and whole-genome duplication[J]. Ann Bot,2022,129(4):457−471. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcac007
[20] Ming TL,Bartholomew B. Polyspora,Flora of China 12[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2007:418−419.
[21] 姚程程,王俊臣,胡继文,肖遥,杨桂娟,等. 香椿种质生长及叶部表型性状的遗传变异分析[J]. 植物科学学报,2020,38(1):112−122. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2020.10112 Yao CC,Wang JC,Hu JW,Xiao Y,Yang GJ,et al. Genetic variation of growth and leaf phenotypic traits of Toona sinensis (A. Juss.) Roem. germplasms[J]. Plant Science Journal,2020,38(1):112−122. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2020.10112
[22] 彭丽平,成仿云,钟原,徐兴兴,鲜宏利. 凤丹栽培群体的表型变异研究[J]. 植物科学学报,2018,36(2):170−180. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2018.20170 Peng LP,Cheng FY,Zhong Y,Xu XX,Xian HL. Phenotypic variation in cultivar populations of Paeonia ostii T. Hong et J. X. Zhang[J]. Plant Science Journal,2018,36(2):170−180. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2018.20170
[23] Sun CW,Wang JW,Duan J,Zhao GC,Weng XH,Jia LM. Association of fruit and seed traits of Sapindus mukorossi germplasm with environmental factors in southern China[J]. Forests,2017,8(12):491. doi: 10.3390/f8120491
[24] 朱弘,朱淑霞,李涌福,伊贤贵,段一凡,等. 尾叶樱桃天然种群叶表型性状变异研究[J]. 植物生态学报,2018,42(12):1168−1178. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2018.0196 Zhu H,Zhu SX,Li YF,Yi XG,Duan YF,et al. Leaf phenotypic variation in natural populations of Cerasus dielsiana[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2018,42(12):1168−1178. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2018.0196
[25] 张腾驹,陈小红,康喜坤,刘静. 四川省珙桐天然种群叶表型多样性[J]. 生态学杂志,2019,38(1):35−43. Zhang TJ,Chen XH,Kang XK,Liu J. Phenotypic diversity of leaf morphologic traits of Davidia involucrata natural populations in Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2019,38(1):35−43.
[26] 艾喆,徐婷婷,周兆娜,马飞. 小叶锦鸡儿天然居群叶形态性状变异研究[J]. 西北植物学报,2020,40(9):1595−1604. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2020.09.1595 Ai Z,Xu TT,Zhou ZN,Ma F. Leaf morphological trait variations in natural populations of Caragana microphylla[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2020,40(9):1595−1604. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2020.09.1595
[27] 汪洋,陈文学,明安觉,雍军,宋丛文,等. 湖北红椿天然种群小叶表型性状变异研究[J]. 植物资源与环境学报,2019,28(2):96−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2019.02.13 Wang Y,Chen WX,Ming AJ,Yong J,Song CW,et al. Study on variation of leaflet phenotypic traits of natural populations of Toona ciliata in Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2019,28(2):96−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2019.02.13
[28] 张晓骁,宋超,张延龙,牛立新,张庆雨,等. 秦岭与子午岭地区紫斑牡丹居群表型多样性研究[J]. 园艺学报,2017,44(1):139−150. Zhang XX,Song C,Zhang YL,Niu LX,Zhang QY,et al. Phenotypic diversity of Paeonia rockii populations in Qinling and Ziwuling Mountain areas[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2017,44(1):139−150.
[29] 张元燕,虞木奎,方炎明. 麻栎不同种源的表型性状变异分析[J]. 植物资源与环境学报,2014,23(3):36−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.03.05 Zhang YY,Yu MK,Fang YM. Analysis on phenotypic trait variation of different provenances of Quercus acutissima[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2014,23(3):36−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.03.05
[30] 李伟,林富荣,郑勇奇,李斌. 皂荚南方天然群体种实表型多样性[J]. 植物生态学报,2013,37(1):61−69. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2013.00007 Li W,Lin FR,Zheng YQ,Li B. Phenotypic diversity of pods and seeds in natural populations of Gleditsia sinensis in southern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2013,37(1):61−69. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2013.00007
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. Qichi Yang,Hehe Zhang,Lihui Wang,Feng Ling,Zhengxiang Wang,Tingting Li,Jinliang Huang. Topography and soil content contribute to plant community composition and structure in subtropical evergreen-deciduous broadleaved mixed forests. Plant Diversity. 2021(04): 264-274 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 董雪,李永华,辛智鸣,段瑞兵,姚斌,包岩峰,黄雅茹,张正国. 河西走廊西段戈壁灌木群落多样性及其分布格局研究. 干旱区地理. 2020(06): 1514-1522 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: