Phenotypic characteristics and comprehensive evaluation of high-quality germplasm resources of Gentiana rigescens Franch. ex Hemsl.
-
摘要:
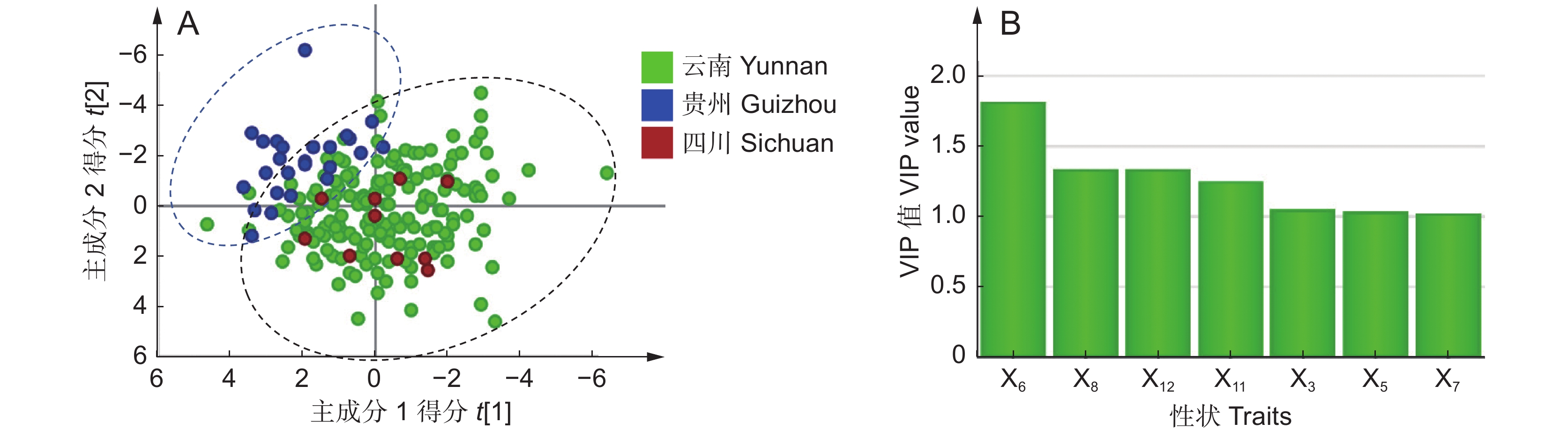
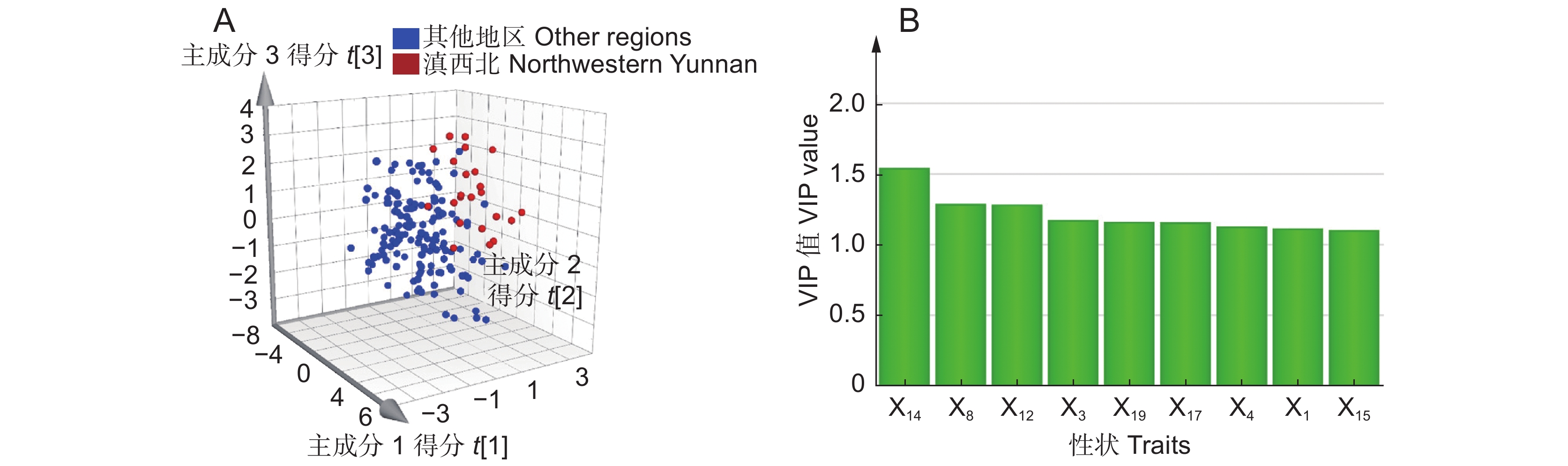
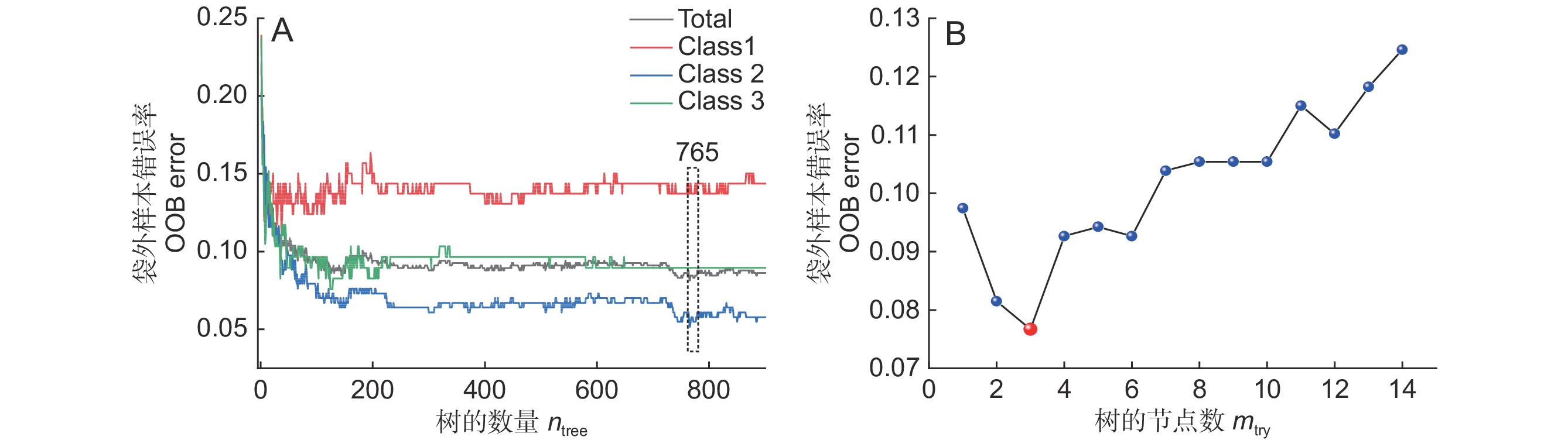
为探讨野生滇龙胆(Gentiana rigescens Franch. ex Hemsl.)优质高产植株性状特征,以采自不同地区的877株滇龙胆为研究材料,利用主成分分析(PCA)、层次聚类(HCA)、隶属函数等方法对有效成分产量性状进行评价。结果显示,17个性状中,根部龙胆苦苷产量多样性指数最高,叶部马钱苷酸和当药苷产量的多样性指数较低;结合隶属函数对所有样品进行评分,发现优质高产种源共214株,占总样品数的24.40%,分布于云南、四川和贵州;变量投影重要性准则(VIP)分析表明,云南与四川的优质种源主要性状特征较为接近,均为当药苷、马钱苷酸及6'-O-β-D-葡萄糖基龙胆苦苷高产;贵州优质种源则为獐牙菜苦苷高产。基于3种机器学习算法建立不同等级种源的鉴别模型,结果发现随机森林(RF)算法建立的判别模型的预测精度和稳定性较高,能对不同等级种源进行有效划分。
Abstract:We explored the phenotypic characteristics and established a classification strategy of high-quality germplasm resources of wild Gentiana rigescens Franch. ex Hemsl. In total, 887 samples of G. rigescens collected from different regions were used as research materials. Principal component analysis (PCA), hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA), and membership function analysis were used to analyze and evaluate 17 active ingredient yield traits of the roots, stems, and leaves. Results showed that gentiopicroside yield in the roots had the highest Shannon-Wiener index value (I = 1.64), while loganic acid and sweroside acid yields in the leaves had the lowest I values (I = 0.73). Based on D value scoring and membership function analysis, we identified 214 high-quality and high-yield seed sources, accounting for 24.40% of the total sample size, distributed in Yunnan, Sichuan, and Guizhou. Variable importance in projection (VIP) analysis showed similar phenotypic characteristics among the high-quality germplasms in Yunnan and Sichuan, which were characterized by high sweroside, loganic acid, and 6'-O-β-D-glucopyranosylgentiopicroside yield. The high-quality germplasms in Guizhou were characterized by high swertiamarin yield. Among the three different machine learning algorithms, results showed that the discrimination model established using the Random Forest (RF) algorithm had the highest prediction accuracy and stability and could effectively identify different provenances.
-
1 如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。2 1 ~ 3)如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。3 1 ~ 3)如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。4 如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。5 1 ~ 3)如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。6 如需查阅附件内容请登录《植物科学学报》网站(http://www.plantscience.cn)查看本期文章。 -
表 1 滇龙胆有效成分产量性状的多样性指数
Table 1 Shannon diversity index of yield traits of active ingredients in Gentiana rigescens
产量性状
Yield traitShannon多样性指数(I) Shannon diversity index 根Root 茎Stem 叶Leaf 马钱苷酸 1.51 0.94 0.73 6'-O-β-D-葡萄糖基龙胆苦苷 1.39 1.15 1.02 獐牙菜苦苷 1.53 1.20 1.09 龙胆苦苷 1.64 1.35 1.05 当药苷 1.37 1.56 0.73 异荭草素 − 1.08 1.05 表 2 基于滇龙胆17个产量性状的主成分分析
Table 2 Principal component analysis results based on 17 yield traits of Gentiana rigescens
成分
Component初始特征值Eigenvalue 特征值
Eigenvalue方差贡献率
Contribution of variance / %累积方差贡献率
Cumulative contribution / %1 7.619 44.816 44.816 2 2.700 15.885 60.700 3 1.602 9.423 70.123 4 1.187 6.982 77.105 5 0.781 4.592 81.697 表 3 基于PLS-DA算法的分类建模评价结果
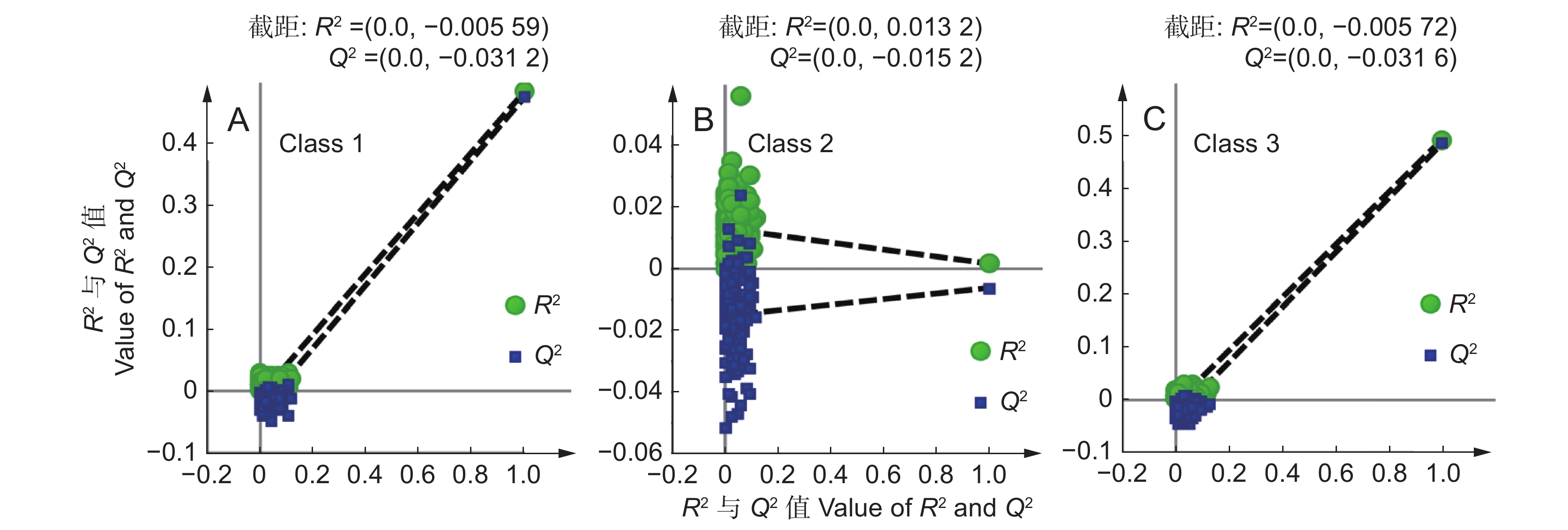
Table 3 Evaluation results of classification model based on PLS-DA algorithm
评价指标
Evaluation parameter一级
Class 1 / %二级
Class 2 / %三级
Class 3 / %合计
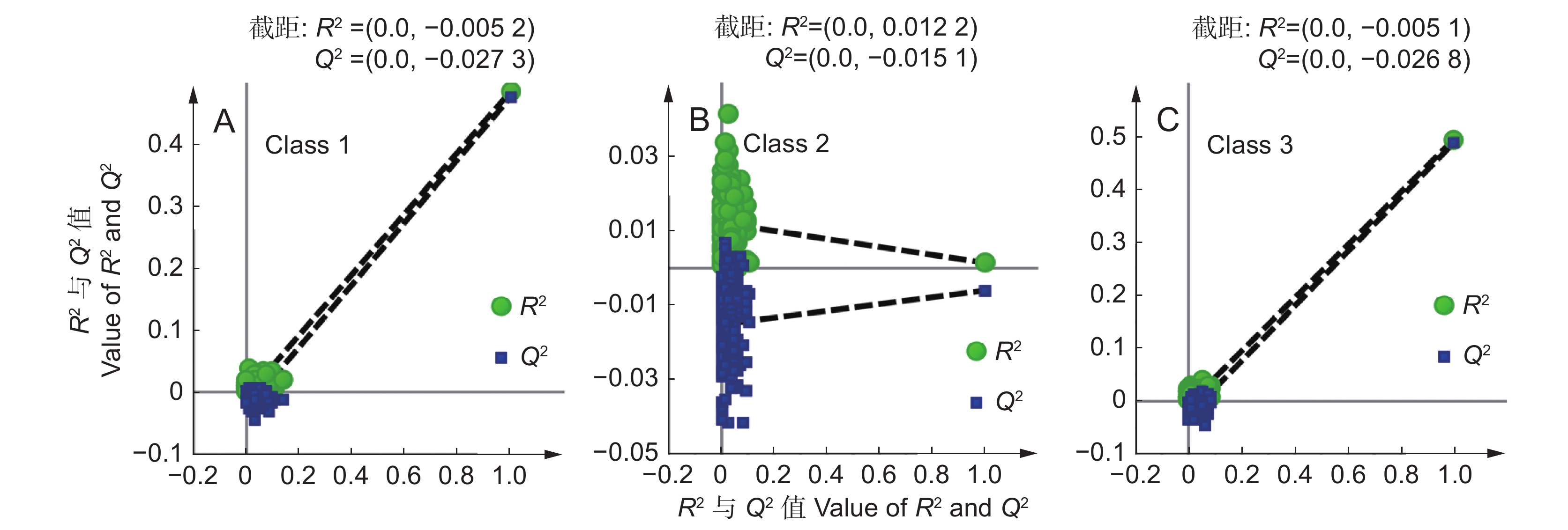
Total / %训练集正确率 92.00 82.24 89.92 88.05 测试集正确率 92.06 86.11 94.05 90.74 注:一级为优质种源,二级为普通种源,三级为劣质种源。下同。 Notes: Classes 1, 2, and 3 refer to high-quality, moderate-quality, and low-quality germplasms, respectively. Same below. 表 4 基于OPLS-DA算法的滇龙胆分类模型
Table 4 Evaluation results of classification model based on OPLS-DA algorithm
评价指标
Evaluation parameter一级
Class 1 / %二级
Class 2 / %三级
Class 3 / %合计
Total / %训练集正确率 92.48 82.24 89.44 88.05 测试集正确率 92.86 86.51 93.65 91.01 表 5 基于随机森林算法建立的滇龙胆分类模型
Table 5 Evaluation results of classification model based on RF algorithm
评价指标
Evaluation parameter一级
Class 1 / %二级
Class 2 / %三级
Class 3 / %合计
Total / %训练集正确率 95.37 91.21 95.85 94.14 测试集正确率 96.43 92.06 95.63 94.71 -
[1] 徐燕玲,王振宇,杨淑达,陆露. 进化生态学在药用植物种质资源评价中的应用与展望[J]. 中草药,2021,52(5):1221−1233. Xu YL,Wang ZY,Yang SD,Lu L. Application and prospect of evolutionary ecology in evaluation of germplasm resources of medicinal plants[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52 (5):1221−1233.
[2] 闫婕,彭成,裴瑾,马云桐,高继海,陈江. 国家中药种质资源库的建设思路与发展策略[J]. 成都中医药大学学报,2021,44(1):14−19,31. Yan J,Peng C,Pei J,Ma YT,Gao JH,Chen J. Construction ideas and development strategies of the state bank of Chinese drug germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,44 (1):14−19,31.
[3] Wang WL,Xu JF,Fang HY,Li ZJ,Li MH. Advances and challenges in medicinal plant breeding[J]. Plant Sci,2020,298:110573. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110573
[4] 刘义飞,胡志刚,黄必胜,陈士林. 组学技术在中药种质资源遗传评价与创新中的应用[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(4):1315−1324. Liu YF,Hu ZG,Huang BS,Chen SL. Application of omics approaches in genetic evaluation and innovation of traditional Chinese medicine germplasm resources[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology,2022,24 (4):1315−1324.
[5] 孟祥才,于鹏程,何录文,关瑜. 从社会发展角度探讨中药资源的历史、现在与未来[J]. 中草药,2022,53(16):5235−5244. Meng XC,Yu PC,He LW,Guan Y. Discussion on past,present and future of traditional Chinese medicine resources based on social development level[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2022,53 (16):5235−5244.
[6] 李智敏,刘莉,李晚谊,张金渝,金航. 滇龙胆的药用资源研究与开发进展[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版),2009,31(S1):485−487,491. Li ZM,Liu L,Li WY,Zhang JY,Jin H. Progress on research and development of G. rigescens as a raw material[J]. Journal of Yunnan University,2009,31 (S1):485−487,491.
[7] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 一部[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 99-100. [8] 褚博文,张霁,李智敏,王元忠. 滇龙胆化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2016,22(13):213−222. Chu BW,Zhang J,Li ZM,Wang YZ. Research advances in chemical constituents and pharmacological activity from Gentiana rigescens[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2016,22 (13):213−222.
[9] 张琳,罗智渊,冯丽丽,李晓东,李海峰. 滇龙胆花药材质量标准及品质评价的研究[J]. 中国药学杂志,2014,49(16):1451−1457. Zhang L,Luo ZY,Feng LL,Li XD,Li HF. Quality evaluation of flowers of Gentiana rigescens Franch.[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2014,49 (16):1451−1457.
[10] 吕伟奇,张霁,左智天,王元忠,张庆芝. 基于灰色关联度分析法的滇龙胆质量评价[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(13):66−73. Lü WQ,Zhang J,Zuo ZT,Wang YZ,Zhang QZ. Quality evaluation of Gentiana rigescens by grey relational analysis method[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2017,23 (13):66−73.
[11] 杨天梅,杨美权,杨绍兵,许宗亮,杨维泽,等. 坚龙胆药材产品质量分级标准研究[J]. 中药材,2018,41(3):648−651. [12] Pan Y,Zhao YL,Zhang J,Li WY,Wang YZ. Phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of the genus Gentiana (Gentianaceae)[J]. Chem Biodivers,2016,13 (2):107−150. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201500333
[13] Shen T,Yu H,Wang YZ. Assessing geographical origin of Gentiana rigescens using untargeted chromatographic fingerprint,data fusion and chemometrics[J]. Molecules,2019,24 (14):2562. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142562
[14] Shen T,Yu H,Wang YZ. Assessing the impacts of climate change and habitat suitability on the distribution and quality of medicinal plant using multiple information integration:take Gentiana rigescens as an example[J]. Ecol Indic,2021,123:107376. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107376
[15] 康传志,张燕,王升,万修福,蒋靖怡,等. 基于多个利益相关方的中药生态农业经济效益分析[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(8):1858−1863. Kang CZ,Zhang Y,Wang S,Wan XF,Jiang JY,et al. Analysis of economic benefits of Chinese medicine eco-agriculture based on multiple stakeholders[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2021,46 (8):1858−1863.
[16] 孟祥才,杜虹韦,魏文峰,霍金海. 中药资源发展存在的问题与对策[J]. 中草药,2018,49(16):3735−3741. Meng XC,Du HW,Wei WF,Huo JH. Problems and countermeasures in development of Chinese materia medica resource[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2018,49 (16):3735−3741.
[17] 段金廒,宿树兰,严辉,郭盛,刘睿,等. 2016−2020年我国中药资源学学科建设及科学研究进展与展望[J]. 中草药,2021,52(17):5151−5165. Duan JA,Su SL,Yan H,Guo S,Liu R,et al. Discipline development and research progress of Chinese medicinal material resources from 2016 to 2020[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52 (17):5151−5165.
[18] 贾瑞玲,赵小琴,南铭,陈富,刘彦明,等. 64份苦荞种质资源农艺性状遗传多样性分析与综合评价[J]. 作物杂志,2021(3):19−27. Jia RL,Zhao XQ,Nan M,Chen F,Liu YM,et al. Genetic diversity analysis and comprehensive assessment of agronomic traits of 64 tartary buckwheat germplasms[J]. Crops,2021 (3):19−27.
[19] Coelho C,Figueredo G,Lafarge C,Bou-Maroun E,Flahaut S. Mid-infrared spectroscopy combined with multivariate analysis and machine-learning:a powerful tool to simultaneously assess geographical origin,growing conditions and bitter content in Gentiana lutea roots[J]. Ind Crops Prod,2022,187:115349. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115349
[20] 宋雪彬,高康,黄河,刘芷兰,戴思兰,嵇彧. 中国传统大菊叶片形态的数量化定义与分类[J]. 植物学报,2021,56(1):10−24. Song XB,Gao K,Huang H,Liu ZL,Dai SL,Ji Y. Quantitative definition and classification of leaves in large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum based on the morphological traits[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany,2021,56 (1):10−24.
[21] Liu CY,Yang ZY,Hu YG. Drought resistance of wheat alien chromosome addition lines evaluated by membership function value based on multiple traits and drought resistance index of grain yield[J]. Field Crops Res,2015,179:103−112. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.04.016
[22] 李红宇,李逸,司洋,杜春颖,周雪松,等. 北方粳稻耐盐碱相关性状主成分分析及综合评价[J]. 核农学报,2020,34(8):1862−1871. Li HY,Li Y,Si Yang,Du CY,Zhou XS,et al. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of saline-alkaline tolerance related traits of northern Japonica rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34 (8):1862−1871.
[23] 王元忠,沈涛,张金渝. 滇重楼及其近缘种的表型变异与资源评价[J]. 热带作物学报,2021,42(9):2535−2541. Wang YZ,Shen T,Zhang JY. Phenotypic variation and resource evaluation of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis and its relative species[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2021,42 (9):2535−2541.
[24] Wang CY,Tang L,Li L,Zhou Q,Li YJ,et al. Geographic authentication of Eucommia ulmoides leaves using multivariate analysis and preliminary study on the compositional response to environment[J]. Front Plant Sci,2020,11:79. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00079
[25] Chen XJ,Min DH,Yasir TA,Hu YG. Evaluation of 14 morphological,yield-related and physiological traits as indicators of drought tolerance in Chinese winter bread wheat revealed by analysis of the membership function value of drought tolerance (MFVD)[J]. Field Crops Res,2012,137:195−201. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2012.09.008
[26] 刘思辰,曹晓宁,温琪汾,王海岗,田翔,等. 山西谷子地方品种农艺性状和品质性状的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2020,53(11):2137−2148. Liu SC,Cao XN,Wen QF,Wang HG,Tian X,et al. Comprehensive evaluation of agronomic traits and quality traits of foxtail millet landrace in Shanxi[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020,53 (11):2137−2148.
[27] 潘晓雪,胡明瑜,王忠伟,吴红,雷开荣. 不同水稻种质资源重要农艺性状与发芽期耐寒性鉴定研究[J]. 作物杂志,2021,37(1):47−53. Pan XX,Hu MY,Wang ZW,Wu H,Lei KR. Evaluation of agronomic traits and cold tolerance at germination stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasms[J]. Crops,2021,37 (1):47−53.
[28] Aneley GM, Haas M, Köhl K. LIDAR-Based phenotyping for drought response and drought tolerance in potato[J]. Potato Res, 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11540-022-09567-8.
[29] Li L,Li ZM,Wang YZ. A method of two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy combined with residual neural network for comparison and differentiation of medicinal plants raw materials superior to traditional machine learning:a case study on Eucommia ulmoides leaves[J]. Plant Methods,2022,18 (1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13007-022-00935-6
[30] Jiang JL,Johansen K,Stanschewski CS,Wellman G,Mousa MAA,et al. Phenotyping a diversity panel of quinoa using UAV-retrieved leaf area index,SPAD-based chlorophyll and a random forest approach[J]. Precis Agric,2022,23 (3):961−983. doi: 10.1007/s11119-021-09870-3
[31] Wu Z,Zhao YL,Zhang J,Wang YZ. Quality assessment of Gentiana rigescens from different geographical origins using FT-IR spectroscopy combined with HPLC[J]. Molecules,2017,22 (7):1238. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071238
[32] Zhao YL,Yuan TJ,Zhang J,Wang YZ. Geographic origin identification and rapid determination of four constituents of Gentiana rigescens by FTIR combined with chemometrics[J]. J Chemometr,2019,33 (4):e3115. doi: 10.1002/cem.3115
[33] Liu L,Zuo ZT,Xu FR,Wang YZ. Study on quality response to environmental factors and geographical traceability of wild Gentiana rigescens Franch.[J]. Front Plant Sci,2020,11:1128. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01128
[34] Parmley KA,Higgins RH,Ganapathysubramanian B,Sarkar S,Singh AK. Machine learning approach for prescriptive plant breeding[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9 (1):17132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53451-4
[35] Rahaman M,Ahsan M,Chen M. Data-mining techniques for image-based plant phenotypic traits identification and classification[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9:19526. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55609-6
[36] Johansen K,Morton MJL,Malbeteau Y,Aragon B,Al-Mashharawi S,et al. Predicting biomass and yield in a tomato phenotyping experiment using UAV imagery and random forest[J]. Front Artif Intel,2020,3:28. doi: 10.3389/frai.2020.00028
[37] 邢晓语,杨秀春,徐斌,金云翔,郭剑,等. 基于随机森林算法的草原地上生物量遥感估算方法研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2021,23(7):1312−1324. Xing XY,Yang XC,Xu B,Jin YX,Guo J,et al. Remote sensing estimation of grassland aboveground biomass based on Random Forest[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2021,23 (7):1312−1324.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 龙桂根,黄芝云,吴南生,冯胜,冯超,丁菲,金松松,何利人,王勇,陈玲. 南酸枣种质资源果实性状变异和综合评价. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2024(06): 781-790 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)
-
其他相关附件
-
PDF格式
沈涛附录 点击下载(515KB)
-



 下载:
下载: